CVA service specifications
![]()
This service employs Change Vector Analysis (Bovolo et Bruzzone, 2007) to derive a binary change detection map from a set of pre- and post-event calibrated assets derived from the same mission.
The tutorial of the CVA service is available in this section.
Service Description
The Change Vector Analysis (CVA) processing service derives a vector of differences between a set of pre- and post-event calibrated assets derived from the same mission.
The CVA algorithm derives from a N-dimensional space magnitude and direction of change between the two input single-band geophysical assets for date 1 and date 2.
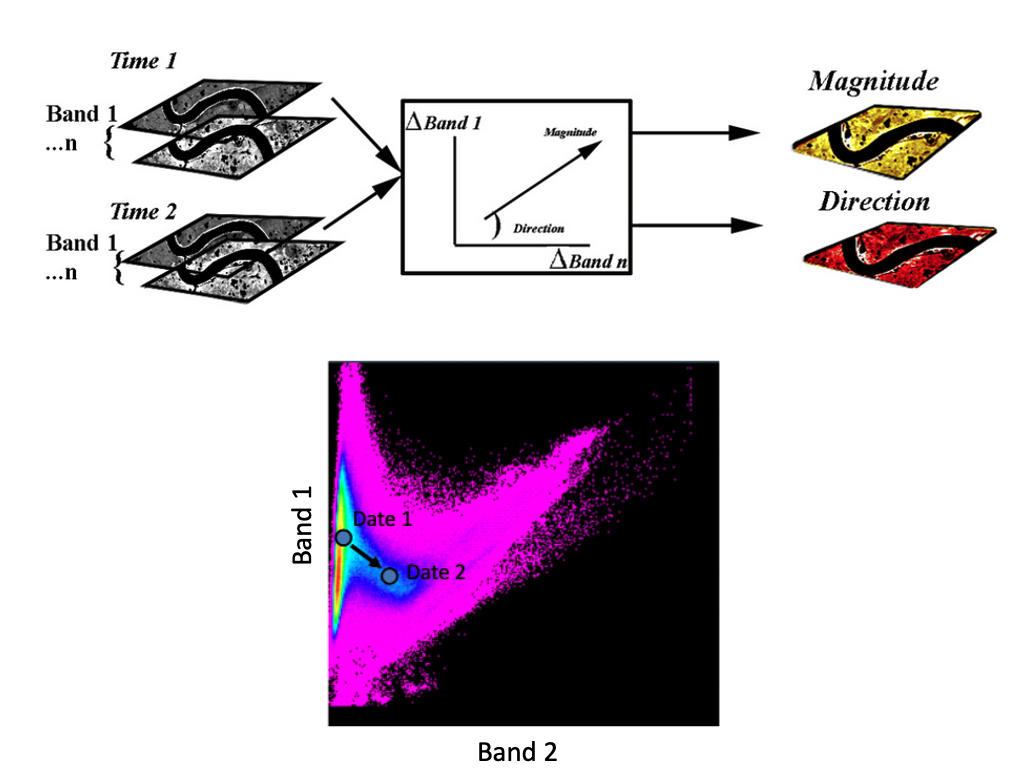
Figure 1 - Schema describing the Change Vector Analysis algorithm. Image credits: Portland State University.
In this change detection service pairs of assets having the same CBN are extracted from pre- and post-event calibrated datasets to make a co-located stack.
Note
CVA requires at least two CBNs from pre- and post-event datasets (minimum 4 assets).
The standardization of inputs is made by removing the mean and scaling to unit variance. Later the CVA1 is applied followed by an automatic thresholding of the multidimensional change detection map based on the Otsu’s method2,3. The Otsu algorithm minimizes the intra-class intensity variance and returns a single intensity threshold which is then employed in the service for the binarization of the change. Thus, the output of the service is a binary map detecting changes before and after the event.
Note
the change detection is applied to all image pixels in the AOI thus clouds and/or water bodies will potentially be part of changes detected. Also change detection results depend on georeferencing accuracy of input pairs of pre- post-event single-band assets. The change detection of the image stack is made after a co-location of input single-band assets without a co-registration.
Inputs
The CVA service requires as input a pair of calibrated Datasets from SAR or Optical missions. Ideally, input SAR Datasets to be made with a pair of Calibrated Datasets from the same mission, track, and polarization.
Warning
This minimum number of single-band geophysical assets must be more than one per Calibrated Dataset. Therefore, CVA requires at least two CBNs from pre- and post-event datasets (minimum 4 assets).
Parameters
The CVA service requires a specified number of mandatory and optional parameters. Table 1 describes the service parameters.
| Parameter | Description | Required | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input pre-event product reference | Pre-event input product to be used in creating the collocated stack and performing CVA. | YES | |
| Input post-event product reference | Post-event input product to be used in creating the collocated stack and performing CVA. | YES | |
| List(s) of comma separated bands | This parameter is a list of bands expressed as a comma separated list of common band names. It defines the list of common band names to extract. List of single band assets to be extracted from the calibrated dataset before and after the event. The service requires the same assets in the pre- and post-event calibrated datasets. | YES | |
| Area of Interest | This parameter defines the area of interest expressed as a Well-Known Text value. If set, it overrides the automatic determination of the maximum common area between the input-reference products geometry. | YES |
Table 1 - Service parameters for the CVA processor.
Input pre- and post-event product references
The pre-event and post-event Calibrated datasets input products to be used in creating the collocated stack and performing CVA.
List-of-comma-separated-bands
This second mandatory parameter is a list of bands expressed as a comma separated list of common band names. The list of single-band geophysical assets to be used for the co-location shall be given as a list of comma separated CBN.
Example
To define multiple reflectance single-band assets from VIS and NIR (e.g. blue, green, red, and nir) from pre- and post-event Calibrated Dataset, the user shall define the 4 input assets in CVA as following:
blue,green,red,nir
AOI
This last parameter may define the area of interest expressed as a Well-Known Text value.
Tip
In the definition of “Area of interest as Well Known Text” it is possible to apply as AOI the drawn polygon defined with the area filter. To do so, click on the button in the left side of the "Area of interest expressed as Well-known text" box and select the option AOI from the list. The platform will automatically fill the parameter value with the rectangular bounding box taken from the current search area in WKT format.
Output
The result product of the CVA service is a single-band change detection binary map (1 change, 0 no change) GeoTIFF in COG format. Product specifications for this service are shown in the below Table.
| Attribute | Value / description |
|---|---|
| Long Name | CVA change detection map |
| Short Name | cva_change_detection |
| Description | Binary change mask: 0=No-change, 1=Change |
| Data Type | 1-bit |
| Band | Single |
| Format | COG |
| Projection | Native or EPSG:4326 - WGS84 |
| Units | N/A |
| Valid Range | [0 - 1] |
Filter and or Vectorize CVA change mask single band asset
CVA's binary change mask asset can be spatially filtered and / or converted to polygon using the FilterVectorize service.
To further post-process the cva_change_detection single band asset by removing small isolated clusters of pixel employ the FilterVectorize service in Filter mode by selecting a filter threshold size value.
The binary change mask can also be converted to polygons by using the FilterVectorize service in Vectorize mode and selecting only true values DN=1 (change).
To apply both spatial filtering and vectorization on CVA's binary change mask employ the FilterVectorize service in the Filter and Vectorize mode.
Warning
Only the cva_change_detection single band asset can be used in the FilterVectorize on-demand service, being the only discrete raster produced by the CVA service.
-
Bovolo F. and Bruzzone L., “A Theoretical Framework for Unsupervised Change Detection Based on Change Vector Analysis in the Polar Domain,” IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., vol. 45, no. 1, pp. 218–236, 2007. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2006.885408. ↩
-
Nobuyuki Otsu (1979). "A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms". IEEE Trans. Sys. Man. Cyber. 9 (1): 62–66. DOI 10.1109/TSMC.1979.4310076. ↩